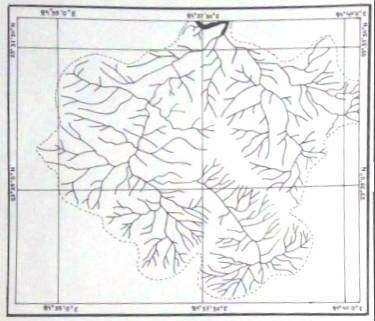
Stream Order
Stream Order:
Stream ordering is a method of assigning a numeric order to links in a stream network. This order is a method for identifying and classifying types of streams based on their numbers of tributaries.
Some characteristics of streams can be inferred by simply knowing their order.
For example, first-order streams are dominated by overland flow of water; they have no upstream
concentrated flow. There are several methods available to assign stream order. Here we followed
the Strahler method (1957) of Stream Ordering.
Strahler method:
In the Strahler method, all links without any tributaries are assigned an order of 1 and are referred to as first order.
The stream order increases when streams of the same order intersect. Therefore, the intersection of two first-order links will create a second-order link, the intersection of two second-order links will create a third-order link, and so on. The intersection of two links of different orders, however, will not result in an increase in order. For example, the intersection of a first-order and second-order link will not create a third-order link but will retain the order of the highest ordered link.
The Strahler method is the most common stream ordering method. However, because this method
only increases in order at intersections of the same order, it does not account for all links and can be sensitive to the addition or removal of links.
Bifurcation Ratio (Rb) :
Bifurcation Ratio is a dimensionless number denoting the ratio between the number of streams of one order and those of the next-higher order in a drainage network. The Bifurcation ratio looks at the relationship between streams of different orders. The Bifurcation Ratio is of fundamental importance in drainage basin analysis as it is the foremost parameter for linking the hydrological regime of a watershed under topological and climatic conditions. It helps in interpreting the shape of the basin and deciphering the run off behaviour. The bifurcation ratio varies from a minimum of 2 in "flat or rolling drainage basins" to 3 or 4 in "mountainous or highly dissected drainage basins"; it is a parameter used in equations giving the number of streams in a basin. Bifurcation ratio may be a useful measure of flood proneness, the higher the bifurcation ratio, the shorter will be the time taken for discharge to reach the outlet, and higher will be the peak discharge leading to a greater probability of flooding. Bifurcation ratio correlates positively withdrainage density i.e., a high bifurcation ratio indicates a high drainage density. Higher Bifurcationratios also suggest that the area is tectonically active.